Describe the Process of Rna Splicing
RNA splicing - The process of excising introns from RNA and connecting the exons into a continuous mRNA. Sharp explains the process of RNA splicing.
Rna Splicing Definition Process Mechanism Types Errors Uses
The final mRNA thus consists of the remaining sequences called exons which are connected to one another through the splicing process.
. When genes are to be expressed by a cell they need to be copied and the non-coding parts edited out before they can be turned into protein. In humans the average length of a gene is 30000 base pairs but the length of a mature. Constitutive splicing is the process of removing introns from the pre-mRNA and joining the exons together to form a mature mRNA.
Occurs during andor after transcription. RNA splicing is the biological process that removes the introns from the primary RNA transcript while ligating the exons together in eukaryotes. Introns are intervening sequences - not expressed in proteins Exons are retained in the mature mRNA molecules.
1 minutes 37 seconds. For nuclear-encoded genes splicing occurs in the nucleus either during or immediately after. It is transcribed by RNA polymerase into pre-mRNA by transcription.
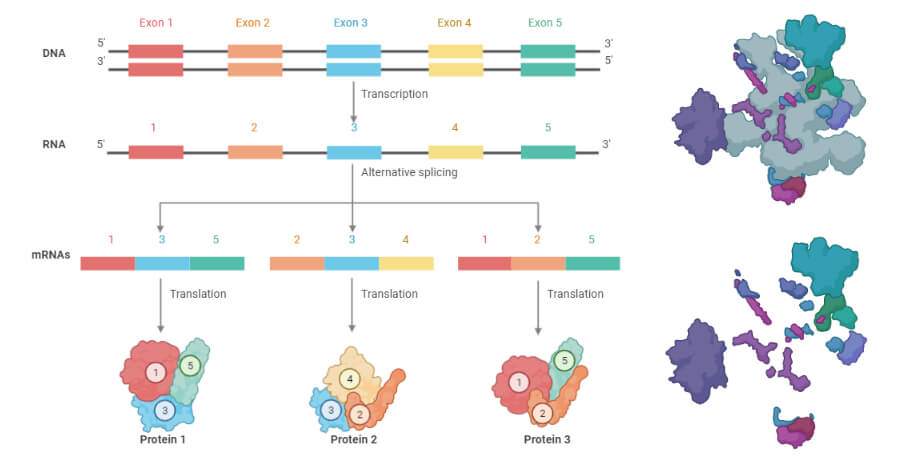
1 Two different modes of splicing have been defined that is constitutive splicing and alternative splicing. An Explanation of RNA Splicing. RNA splicing is a modification process of the nascent precursor messenger RNA transcript in which the introns are removed and exons are joined.
It produces a final draft of the mRNA before translation gets under way. This process is called RNA splicing. These regions are mixed together and the introns must.
In splicing some sections of the RNA transcript introns are removed and the remaining sections exons are stuck back together. In plants certain chloroplast and mitochondrial genes encoding either tRNAs or proteins are interrupted by introns. Splicing is mediated by the spliceosome which consists of several protein-RNA complexes.
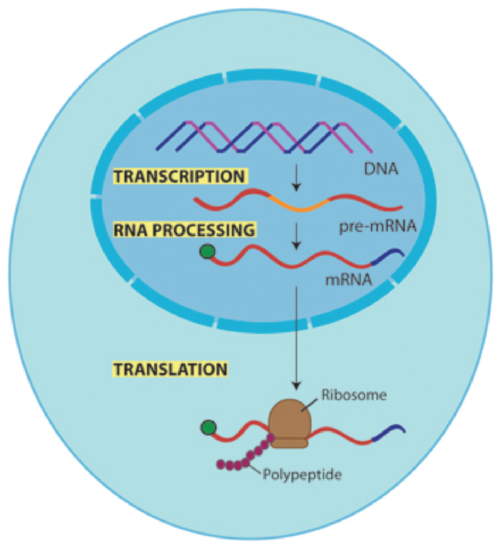
HnRNA is processed in the nucleus and converted to mRNA which then comes to the cytoplasm and undergoes translation or protein synthesis. The first step involves two complexes that bind near the GU sequence. 3D Animation of DNA to RNA to Protein.
RNA splicing was initially discovered in the 1970s. The process of splicing fundamentally changes the information content of the RNA transcript which directly impacts translation of that genetic information. The Connection Between SMA and RNA Splicing.
It is a post-transcriptional modification. RNA splicing RNA is called hnRNA - Heteronuclear RNA before splicing occurs Splicing is. This process is called RNA splicing.
RNA splicing removes the introns from pre mRNA to produce the final set of instructions for the protein. As DNA is transcribed into RNA it needs to be edited to remove non-coding regions or introns shown in green. This final complex then undergoes a.
Select the description of RNA splicing. This process can take place either co-transcriptionally or post-transcriptionally. Describe the Nuclear Splice Sites Are Short Sequences in human GU-AG introns.
This editing process is called splicing which involves removing the introns leaving only the. When and where RNA splicing takes place in the cell represents a central question of cell biology. RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA pre-mRNA transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA It works by removing all the introns non-coding regions of RNA and splicing back together exons coding regions.
This final complex then undergoes a. The RNA folds in away that forms a guanine-binding pocket which allows the molecule to bind a free guanine nucleotide and use that to initiate splicing. Co-transcriptional splicing allows functional integration of transcription and RNA processing machineries and could allow them to modulate one another whereas post-transcriptional.
RNA splicing is the removal of introns and joining of exons in eukaryotic mRNA. Group II Introns Protein-encoding genes in mitochondria and chloroplasts. The first step involves two complexes that bind near the GU sequence.
The process by which RNA is created from a DNA template the process by which a polypeptide is synthesized using the genetic information encoded in mature mRNA the process by which a 5 cap is added to one end of an mRNA molecule and a poly-A tail is added to the other the process by which noncoding regions. The RNA in then looped and three other protein-RNA complexes bind. In normal splicing a special protein and RNA complex called the spliceosome attaches itself to the primary mRNA.
The RNA in then looped and three other protein-RNA complexes bind. Sharp and Sumner describe how RNA splicing can be used as a therapy for SMA. ÐThe mechanism by which introns are removed.
Some genes can be alternatively spliced leading to the production of different mature mRNA molecules from the same initial transcript. Splicing is mediated by the spliceosome which consists of several protein-RNA complexes. RNA splicing a post-transcriptional process necessary to form a mature mRNA was discovered in the late 1970s.
In splicing specific regions of the RNA transcript are cut out and the flanking sequences are pasted together. RNA splicing is the process by which the newly synthesized pre-mRNA also known as hnRNA heterogeneous nuclear RNA is processed and forms the mature mRNA. The primary mRNA has various regions called introns and exons.
The pre-mRNA is undergone post transcriptional modifications where introns are spliced out from mRNA. RNA splicing is a process in eukaryotic gene expression where that genetic information is altered while in RNA form.

Mrna Splicing Biology Libretexts



Comments
Post a Comment